Keys
- Keys play an important role in the relational database.
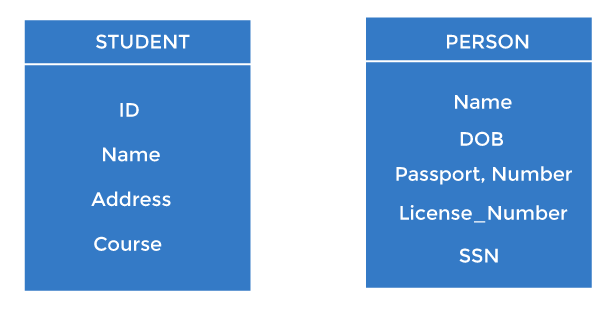
- It is used to uniquely identify any record or row of data from the table. It is also used to establish and identify relationships between tables.
For example, ID is used as a key in the Student table because it is unique for each student. In the PERSON table, passport_number, license_number, and SSNand are keys since they are unique for each person.
Types of keys:
1. Primary key
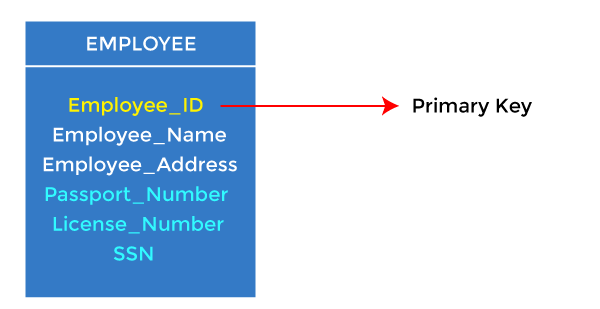
- It is the first key used to identify one and only one instance of an entity uniquely. An entity can contain multiple keys, as we saw in the PERSON table. The key which is most suitable from those lists becomes the primary key.
- In the EMPLOYEE table, ID can be the primary key since it is unique for each employee. In the EMPLOYEE table, we can even select License_Number and Passport_Number as primary keys since they are also unique.
- For each entity, the primary key selection is based on requirements and developers.
2. Candidate key
- A candidate key is an attribute or set of attributes that can uniquely identify a tuple.
- Except for the primary key, the remaining attributes are considered candidate keys. The candidate keys are as strong as the primary key.
For example: In the EMPLOYEE table, id is best suited for the primary key. The rest of the attributes, like SSN, Passport_Number, License_Number, etc., are considered candidate keys.

3. Super Key
A super key is an attribute set that can uniquely identify a tuple. A super key is a superset of a candidate key.
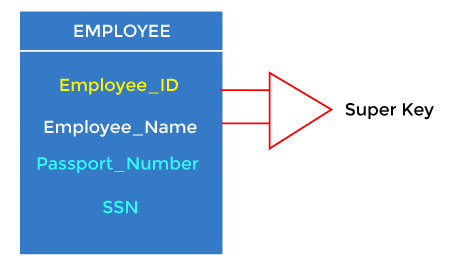
For example: In the above EMPLOYEE table, for(EMPLOEE_ID, EMPLOYEE_NAME), the name of two employees can be the same, but their EMPLYEE_ID can't be the same. Hence, this combination can also be a key.
The super key would be EMPLOYEE-ID (EMPLOYEE_ID, EMPLOYEE-NAME), etc.
4. Foreign key
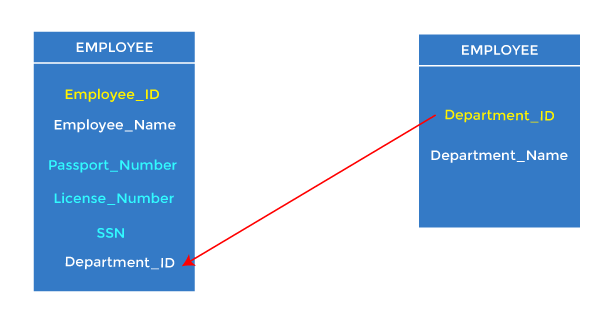
- Foreign keys are the column of the table used to point to the primary key of another table.
- Every employee works in a specific department in a company, and employee and department are two different entities. So we can't store the department's information on the employee table. That's why we link these two tables through the primary key of one table.
- We add the primary key of the DEPARTMENT table, Department_Id, as a new attribute in the EMPLOYEE table.
- In the EMPLOYEE table, Department_Id is the foreign key, and both the tables are related.
5. Alternate key
There may be one or more attributes or a combination of attributes that uniquely identify each tuple in a relation. These attributes or combinations of the attributes are called the candidate keys. One key is chosen as the primary key from these candidate keys, and the remaining candidate key, if it exists, is termed the alternate key. In other words, the total number of alternate keys is the total number of candidate keys minus the primary key. The alternate key may or may not exist. If there is only one candidate key in a relation, it does not have an alternate key.
For example, employee relation has two attributes, Employee_Id and PAN_No, that act as candidate keys. In this relation, Employee_Id is chosen as the primary key, so the other candidate key, PAN_No, acts as the Alternate key.

6. Composite key
Whenever a primary key consists of more than one attribute, it is known as a composite key. This key is also known as Concatenated Key.
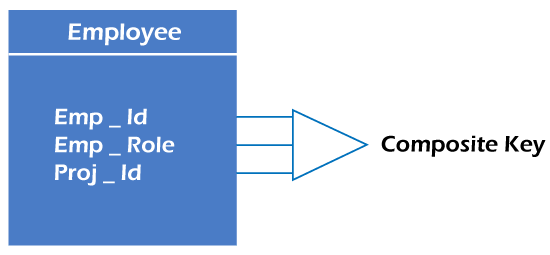
For example, in employee relations, we assume that an employee may be assigned multiple roles, and an employee may work on multiple projects simultaneously. So the primary key will be composed of all three attributes, namely Emp_ID, Emp_role, and Proj_ID in combination. So these attributes act as a composite key since the primary key comprises more than one attribute.
7. Artificial key
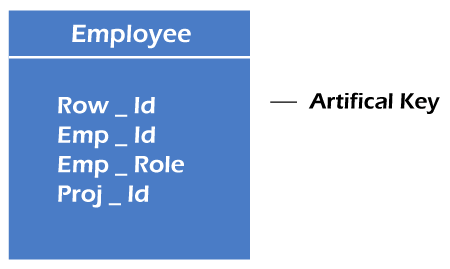
The key created using arbitrarily assigned data are known as artificial keys. These keys are created when a primary key is large and complex and has no relationship with many other relations. The data values of the artificial keys are usually numbered in a serial order.
For example, the primary key, which is composed of Emp_ID, Emp_role, and Proj_ID, is large in employee relations. So it would be better to add a new virtual attribute to identify each tuple in the relation uniquely.


0 comments:
Post a Comment
Thanks