Python Tuple
Python Tuple is used to store the sequence of immutable Python objects. The tuple is similar to lists since the value of the items stored in the list can be changed, whereas the tuple is immutable, and the value of the items stored in the tuple cannot be changed.
Creating a tuple
A tuple can be written as the collection of comma-separated (,) values enclosed with the small () brackets. The parentheses are optional but it is good practice to use. A tuple can be defined as follows.
Output:
<class 'tuple'> <class 'tuple'> <class 'tuple'>
Note: The tuple which is created without using parentheses is also known as tuple packing.
An empty tuple can be created as follows.
Creating a tuple with single element is slightly different. We will need to put comma after the element to declare the tuple.
Output:
<class 'str'> <class 'tuple'>
A tuple is indexed in the same way as the lists. The items in the tuple can be accessed by using their specific index value.
Consider the following example of tuple:
Example - 1
Output:
(10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60) tuple1[0] = 10 tuple1[1] = 20 tuple1[2] = 30 tuple1[3] = 40 tuple1[4] = 50 tuple1[5] = 60
Example - 2
Output:
Enter the tuple elements ...123456
('1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6')
tuple1[0] = 1
tuple1[1] = 2
tuple1[2] = 3
tuple1[3] = 4
tuple1[4] = 5
tuple1[5] = 6
A tuple is indexed in the same way as the lists. The items in the tuple can be accessed by using their specific index value.
We will see all these aspects of tuple in this section of the tutorial.
Tuple indexing and slicing
The indexing and slicing in the tuple are similar to lists. The indexing in the tuple starts from 0 and goes to length(tuple) - 1.
The items in the tuple can be accessed by using the index [] operator. Python also allows us to use the colon operator to access multiple items in the tuple.
Consider the following image to understand the indexing and slicing in detail.
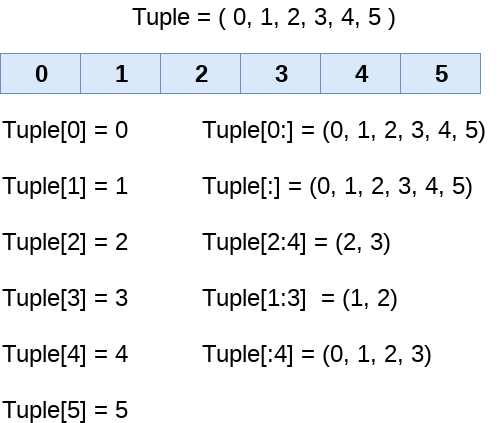
Consider the following example:
Output:
1 2 3 tuple index out of range
In the above code, the tuple has 7 elements which denote 0 to 6. We tried to access an element outside of tuple that raised an IndexError.
Output:
(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) (1, 2, 3, 4) (1, 2, 3, 4) (1, 3, 5)
Negative Indexing
The tuple element can also access by using negative indexing. The index of -1 denotes the rightmost element and -2 to the second last item and so on.
The elements from left to right are traversed using the negative indexing. Consider the following example:
Output:
5 2 (3, 4) (1, 2, 3, 4) (4, 5)
Deleting Tuple
Unlike lists, the tuple items cannot be deleted by using the del keyword as tuples are immutable. To delete an entire tuple, we can use the del keyword with the tuple name.
Consider the following example.
Output:
(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "tuple.py", line 4, in <module>
print(tuple1)
NameError: name 'tuple1' is not defined
Basic Tuple operations
The operators like concatenation (+), repetition (*), Membership (in) works in the same way as they work with the list. Consider the following table for more detail.
Let's say Tuple t = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) and Tuple t1 = (6, 7, 8, 9) are declared.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Repetition | The repetition operator enables the tuple elements to be repeated multiple times. | T1*2 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) |
| Concatenation | It concatenates the tuple mentioned on either side of the operator. | T1+T2 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) |
| Membership | It returns true if a particular item exists in the tuple otherwise false | print (2 in T1) prints True. |
| Iteration | The for loop is used to iterate over the tuple elements. | for i in T1:
print(i)Output1 2 3 4 5 |
| Length | It is used to get the length of the tuple. | len(T1) = 5 |
Python Tuple inbuilt functions
| SN | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | cmp(tuple1, tuple2) | It compares two tuples and returns true if tuple1 is greater than tuple2 otherwise false. |
| 2 | len(tuple) | It calculates the length of the tuple. |
| 3 | max(tuple) | It returns the maximum element of the tuple |
| 4 | min(tuple) | It returns the minimum element of the tuple. |
| 5 | tuple(seq) | It converts the specified sequence to the tuple. |
Where use tuple?
Using tuple instead of list is used in the following scenario.
1. Using tuple instead of list gives us a clear idea that tuple data is constant and must not be changed.
2. Tuple can simulate a dictionary without keys. Consider the following nested structure, which can be used as a dictionary.
List vs. Tuple
| SN | List | Tuple |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The literal syntax of list is shown by the []. | The literal syntax of the tuple is shown by the (). |
| 2 | The List is mutable. | The tuple is immutable. |
| 3 | The List has the a variable length. | The tuple has the fixed length. |
| 4 | The list provides more functionality than a tuple. | The tuple provides less functionality than the list. |
| 5 | The list is used in the scenario in which we need to store the simple collections with no constraints where the value of the items can be changed. | The tuple is used in the cases where we need to store the read-only collections i.e., the value of the items cannot be changed. It can be used as the key inside the dictionary. |
| 6 | The lists are less memory efficient than a tuple. | The tuples are more memory efficient because of its immutability. |

0 comments:
Post a Comment
Thanks