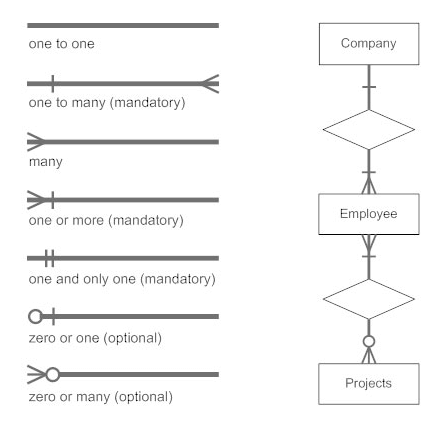
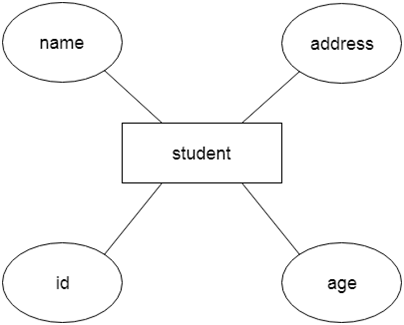
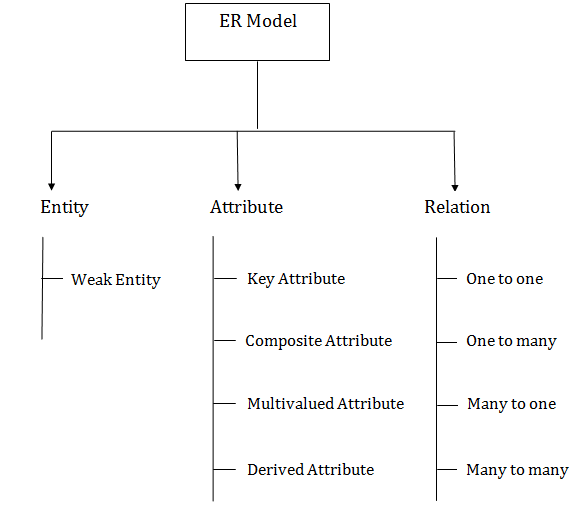
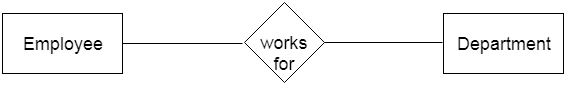
Relational Model concept
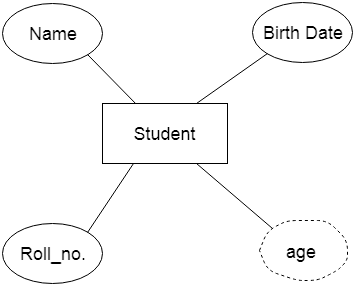
The relational model can represent as a table with columns and rows. Each row is known as a tuple. Each table of the column has a name or attribute.
Domain: It contains a set of atomic values that an attribute can take.
Attribute: It contains the name of a column in a particular table. Each attribute Ai must have a domain, dom(Ai)
Relational instance: In the relational database system, the relational instance is represented by a finite set of tuples. Relation instances do not have duplicate tuples.
Relational schema: A relational schema contains the name of the relation and the name of all columns or attributes.
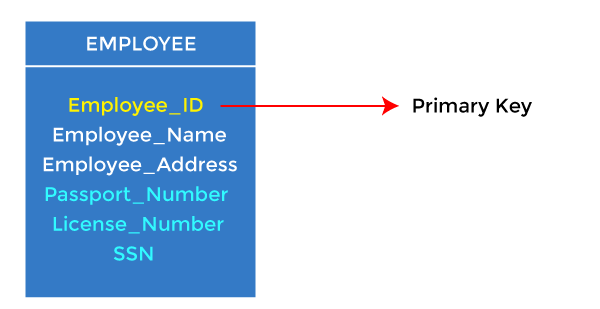
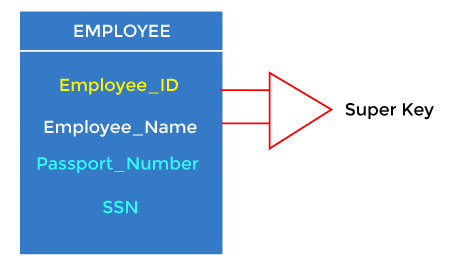
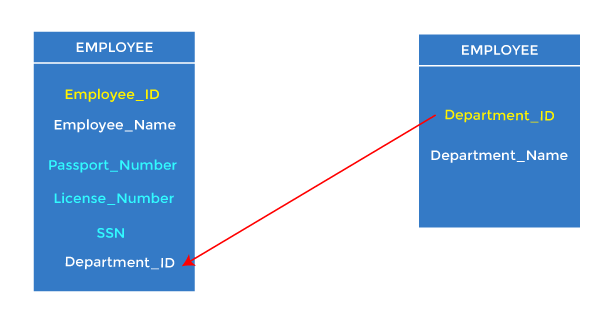
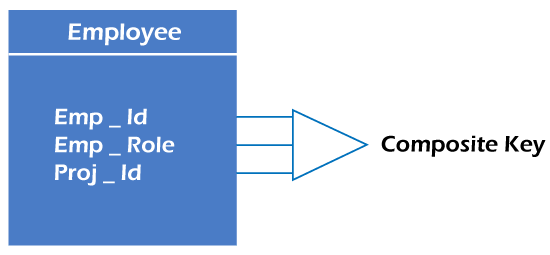
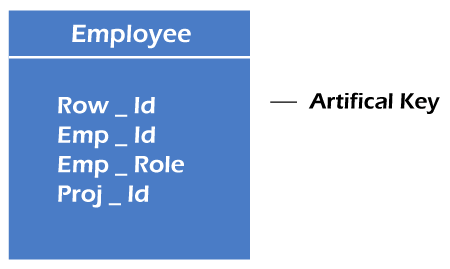
Relational key: In the relational key, each row has one or more attributes. It can identify the row in the relation uniquely.
Example: STUDENT Relation
| NAME | ROLL_NO | PHONE_NO | ADDRESS | AGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ram | 14795 | 7305758992 | Noida | 24 |
| Shyam | 12839 | 9026288936 | Delhi | 35 |
| Laxman | 33289 | 8583287182 | Gurugram | 20 |
| Mahesh | 27857 | 7086819134 | Ghaziabad | 27 |
| Ganesh | 17282 | 9028 9i3988 | Delhi | 40 |
- In the given table, NAME, ROLL_NO, PHONE_NO, ADDRESS, and AGE are the attributes.
- The instance of schema STUDENT has 5 tuples.
- t3 = <Laxman, 33289, 8583287182, Gurugram, 20>
Properties of Relations
- The name of the relation is distinct from all other relations.
- Each relation cell contains exactly one atomic (single) value
- Each attribute contains a distinct name
- The attribute domain has no significance
- tuple has no duplicate value
- The order of tuple can have a different sequence