Vue.js Watch Property
The Vue.js Watcher or watch property allows the developers to listen to the component data and run whenever they change a particular property. The watcher or watch property is a unique Vue.js feature that lets you keep an eye on one property of the component state and run a function when that property value changes.
Let's take an example to see and learn about the Watch property in VueJS. See the following examples to understand the concept of watcher or watch property.
Index.html file:
Index.js file:
Let's use a simple CSS file to make the output more attractive.
Index.css file:
After the execution of the program, you will see the following output:
Output:
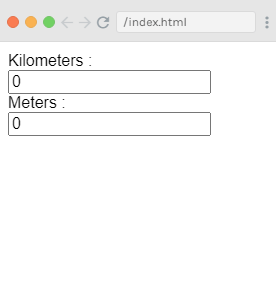
You can see that the output has the 0 entry in its textboxes. If you enter some values in the kilometers textbox you can see the changes in the meters textbox and vice-versa. Let's enter 50 in kilometers textbox and see the result.
Output:
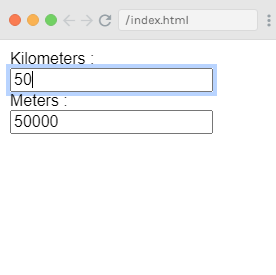
Now, enter some value in the meter textbox and see the changes in the kilometers textbox. Let's enter 5 in the meter textbox and see the result in the output.
Output:
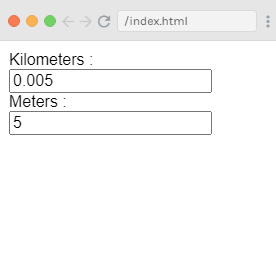
Example Explanation
In the above example, we have created two textboxes, one with kilometers and another with meters. We have initialized both textboxes the kilometers and meters to 0 in the data property. Here, we have created a watch object created with two functions kilometers and meters. In both the functions, the conversion from kilometers to meters and from meters to kilometers is done.
When you enter values inside any of the textboxes, whichever is changed, the Watch property takes care of updating both the textboxes. You do not have to assign any events or wait for it to change and do the extra work of validating. The watch property takes care of updating the textboxes with the calculation done in the respective functions.
Vue.js Computed vs. Watched Property
If you compare Vue.js computed property with Vue.js watch property, then the Vue.js watch property provides a more generic way to observe and react to data changes.
If you have some data that you need to change based on some other data, it is easy and straightforward to use watch property, especially if you are coming from an AngularJS background. But, it is a better idea to use a computed property rather than an imperative watch callback.
Let's take an example and see and compare it with both watch property and computed property.
Index.html file:
Index.js file:
Output:
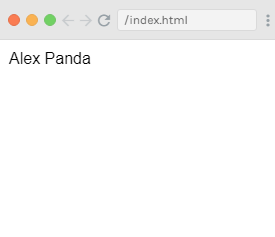
You can see that the above code is imperative and repetitive. Now, let's compare it with a computed property example:
Index.html file:
Index.js file:
Output:
You can see that both examples give the same result, but the second one, "computer property" example is much better and concise.
by : javatpoint



0 comments:
Post a Comment
Thanks