DBMS Architecture
- The DBMS design depends upon its architecture. The basic client/server architecture is used to deal with a large number of PCs, web servers, database servers, and other components that are connected with networks.
- The client/server architecture consists of many PCs and a workstation that are connected via the network.
- DBMS architecture depends upon how users are connected to the database to get their requests done.
Types of DBMS Architecture
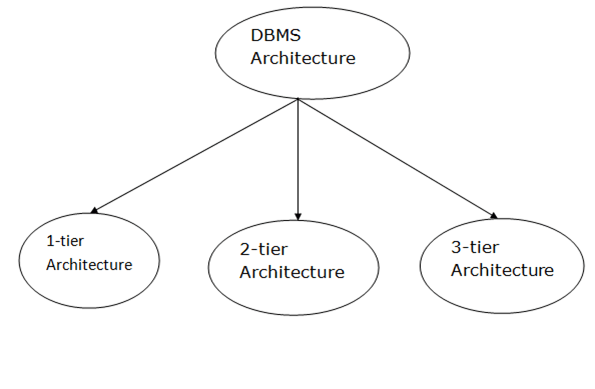
Database architecture can be seen as a single-tier or multi-tier. But logically, database architecture is of two types: 2-tier architecture and 3-tier architecture.
1-Tier Architecture
- In this architecture, the database is directly available to the user. It means the user can directly sit on the DBMS and uses it.
- Any changes done here will directly be done on the database itself. It doesn't provide a handy tool for end-users.
- The 1-Tier architecture is used for the development of the local application, where programmers can directly communicate with the database for a quick response.
2-Tier Architecture
- The 2-Tier architecture is the same as the basic client-server. In the two-tier architecture, applications on the client end can directly communicate with the database on the server-side. For this interaction, APIs like ODBC, and JDBC are used.
- The user interfaces and application programs are run on the client-side.
- The server side is responsible to provide the functionalities like query processing and transaction management.
- To communicate with the DBMS, the client-side application establishes a connection with the server-side.
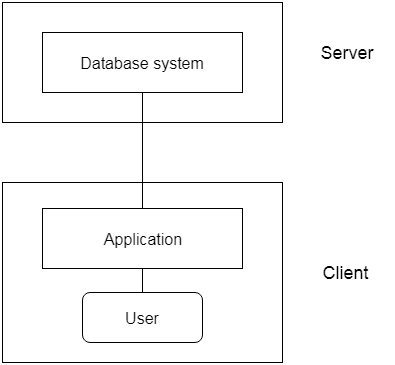
Fig: 2-tier Architecture
3-Tier Architecture
- The 3-Tier architecture contains another layer between the client and server. In this architecture, the client can't directly communicate with the server.
- The application on the client-end interacts with an application server which further communicates with the database system.
- The end user has no idea about the existence of the database beyond the application server. The database also has no idea about any other user beyond the application.
- The 3-Tier architecture is used in the case of the large web applications.
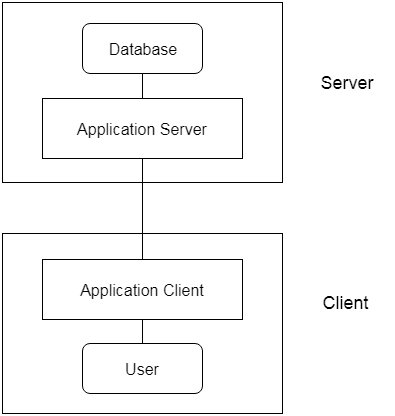
Fig: 3-tier Architecture

0 comments:
Post a Comment
Thanks