Python While loop
The Python while loop allows a part of the code to be executed until the given condition returns false. It is also known as a pre-tested loop.
It can be viewed as a repeating if statement. When we don't know the number of iterations then the while loop is the most effective to use.
The syntax is given below.
Here, the statements can be a single statement or a group of statements. The expression should be any valid Python expression resulting in true or false. The true is any non-zero value and the false is 0.
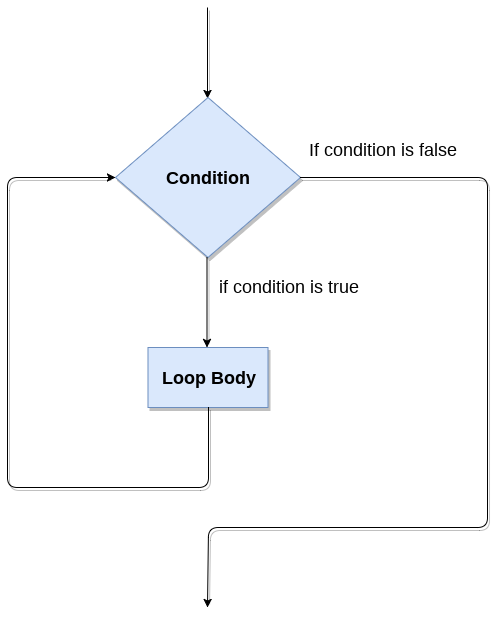
While loop Flowchart
Loop Control Statements
We can change the normal sequence of the while loop's execution using the loop control statement. When the while loop's execution is completed, all automatic objects defined in that scope are demolished. Python offers the following control statement to use within the while loop.
1. Continue Statement - When the continue statement is encountered, the control transfer to the beginning of the loop. Let's understand the following example.
Example:
Output:
Current Letter: j Current Letter: v Current Letter : p Current Letter: o Current Letter: i Current Letter: n
2. Break Statement - When the break statement is encountered, it brings control out of the loop.
Example:
Output:
Current Letter: j Current Letter : a Current Letter : v Current Letter : a
3. Pass Statement - The pass statement is used to declare the empty loop. It is also used to define empty class, function, and control statement. Let's understand the following example.
Example -
Output:
Value of i : 10
Example-1: Program to print 1 to 10 using while loop
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Example -2: Program to print table of given numbers.
Output:
Enter the number:10 10 X 1 = 10 10 X 2 = 20 10 X 3 = 30 10 X 4 = 40 10 X 5 = 50 10 X 6 = 60 10 X 7 = 70 10 X 8 = 80 10 X 9 = 90 10 X 10 = 100
Infinite while loop
If the condition is given in the while loop never becomes false, then the while loop will never terminate, and it turns into the infinite while loop.
Any non-zero value in the while loop indicates an always-true condition, whereas zero indicates the always-false condition. This type of approach is useful if we want our program to run continuously in the loop without any disturbance.
Example 1
Output:
Hi! we are inside the infinite while loop Hi! we are inside the infinite while loop
Example 2
Output:
Enter the number:10 Entered value is 10 Enter the number:10 Entered value is 10 Enter the number:10 Entered value is 10 Infinite time
Using else with while loop
Python allows us to use the else statement with the while loop also. The else block is executed when the condition given in the while statement becomes false. Like for loop, if the while loop is broken using break statement, then the else block will not be executed, and the statement present after else block will be executed. The else statement is optional to use with the while loop. Consider the following example.
Example 1
Example 2
Output:
1 2
In the above code, when the break statement encountered, then while loop stopped its execution and skipped the else statement.
Example-3 Program to print Fibonacci numbers to given limit
Output:
Enter the terms 10 Fibonacci sequence: 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34

0 comments:
Post a Comment
Thanks